Authored by Zachary Yost via The Mises Institute,
“Never let a crisis go to waste,” the old adage goes, and the coronavirus fiasco has demonstrated this principle in action more times than one can count. From declarations of veritable society-wide house arrest to crazed government spending and monetary policy, there has been no shortage of opportunistic actors working to live out their dreams of power and dominion over others that “normal” times would not allow.
Another such instance of gleeful advantage taking has come to light in the form of the Pennsylvania Department of Health’s “Ethical Allocation Framework for Emerging Treatments of COVID-19” guideline, a document that barely conceals its authors’ desire to use the current fiasco as an opportunity to engage in their own schemes of egalitarian social engineering.
Just as a reminder of the kind of central planners we are dealing with, this is the same Pennsylvania Department of Health that decreed on May 12 that nursing homes “must continue to take new admissions, if appropriate beds are available, and a suspected or confirmed positive for COVID-19 is not a reason to deny admission.” Months later, nearly 70 percent of coronavirus fatalities in the state have occurred in nursing homes.
Not being content with causing such a disaster, the state health department has issued guidance on how healthcare facilities should ration the limited supply of the new drug Remdesivir in the event that there are not enough doses to go around, but notes that the guidelines should apply to any scarce form of treatment. While certainly an unpleasant subject to address, it is true that in the face of scarcity the limited supply of Remdesivir or any other treatment will need to be rationed and that some kind of method of choosing will be needed. Scarcity is simply a fact of life that must be dealt with. However, because the distribution of Remdisivir has been taken over by the federal government, which distributes it to state governments, which in turn distribute it to healthcare providers, the process has unavoidably become political.
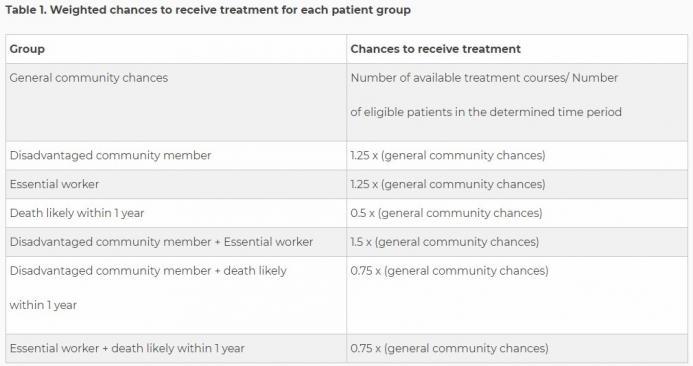
Putting all the jargon aside, the guideline is very clear about several points. First, it is not considered acceptable to distribute care via a random lottery, or on a first-come-first-served basis. Rather, healthcare providers must take into consideration “community-benefit” when rationing care and the department recommends the use of a weighted lottery system.
As you can see, the example lottery that the health department provides uses three different criteria to determine how a patient’s lottery chance is weighted: membership in a disadvantaged community, being an essential worker, and likelihood of death in the next year.
While the state’s determination of who is and who is not an essential worker is arbitrary and has been full of problems, one can at least see the logic behind such a consideration, as well as for those patients who are not likely to live much longer, although one must question where the state gets the authority to dictate such things to hospitals.
What raises the most concern is the idea that members of “disadvantaged communities” should be given a better chance at receiving treatment than others.
According to the guidance, because “low-income communities and certain racial/ethnic minorities” are being disproportionately burdened by the coronavirus, the end goal of public health is served by benefitting some groups over others.
According to the guidance, “the rationale is that a core goal of public health is to redress inequities that make health and safety less accessible to disadvantaged groups.”
One might have thought that the main goal of public health was to save as many lives as possible. But instead, it seems that the state department of health considers the emergency room to be the perfect place to start “mitigating the structural inequities that cause certain communities to bear the greatest burden during the pandemic.”
This formulation makes it unclear what the guidance means when it states that the first goal of the ethical framework is “to safeguard the public’s health by allocating scarce treatments to maximize community benefit.” Does community benefit mean saving as many lives as possible? Or is it some kind of grievance studies conception of equality where arriving at a more “equally distributed” survival rate based on race and socioeconomic status is the goal?
One can certainly argue that certain populations do not have very good access to healthcare resources, but it seems outrageous to think that the time to attempt to remedy such inequality is when triaging patients.
Similarly concerning is the way the guidance recommends that the treating physicians be removed from the rationing process and that it be left in the hands of hospital bureaucrats instead, effectively tying doctors’ hands to treat their patients. Is this the kind of state-run healthcare that we have to look forward to in the future? Doctors as helpless as their patients as bureaucrats “assess” a patient’s social suitability to be worthy of treatment?
The guidance goes on to recommend some procedures for how membership in a “disadvantaged community” should be determined. After noting that both members of low-income communities and racial minorities have been adversely affected by the virus and therefore deserve an increased chance of receiving treatment, the racial component drops entirely from consideration in recommendations, no doubt because such discrimination would be highly illegal and result in a torrent of lawsuits against the state and any hospital foolish enough to try it. The guideline is explicit that “no one is excluded from access based on age, disability, religion, race, ethnicity, national origin, immigration status, gender, sexual orientation, or gender identity and to ensure that no one is denied access based on stereotypes, perceived quality of life, or judgments about a person’s worth.” However, one can’t help but think that if racial discrimination were not illegal the logic of this guidance would dictate that it be undertaken in the name of “equality.”
What that list is lacking is a prohibition on discrimination based on socioeconomic status, which is the method the guidance suggests should be used for the purposes of weighing the lottery. Specifically, it recommends the use of the Area Deprivation Index, which is based on data from the 2015 American Community Survey. Hospitals would use the index’s Neighborhood Atlas to enter a patient’s address and determine if they are a disadvantaged community member.
One can’t help but feel that such a system is arbitrary to the extreme. When I entered my address into the Neighborhood Atlas I discovered that no one in my neighborhood would receive any weighted advantage if Remdisivir were needed. However, when I Google mapped the distance between my home and the nearest sector considered to be disadvantaged, I discovered that it was a mere two-minute drive away. Can anything based on something so arbitrary as five-year-old aggregated census block data be considered a useful tool for the fair rationing of treatment?
This entire scheme is just a taste of the ways medical care would be infected with politics if it were to be run by the government. In a system of socialized medicine would we see similar redistributionist schemes of rationing introduced? No doubt, many people of all political persuasions would view it as a fertile field for attempts at social engineering. Similarly, it is not hard to see politicians scheming to ensure that favored constituents and voting blocs have access to care at the expense of their opponent’s supporters, or that whole classes of people are purposefully and consciously disadvantaged based on whoever holds the keys to power at the moment.
The middle of a pandemic is no time for social engineering, but it is also not a time for state involvement in healthcare to begin with. That involvement has led to thousands of nursing home patients dying and has now led to a blatant redistributionist drug-rationing scheme. Further involvement is only going to make matters worse and continue to poison a crucial aspect of our lives with politics even more than it already is.