Authored by Niall Ferguson, op-ed via Bloomberg.com,
Fires, blackouts, high taxes, poverty, scarce housing, urban squalor, lousy schools – it’s a wonder anybody stays.
“California, folks, is America fast forward.” Thus Governor Gavin Newsom, hoarsely, amid brown smoke at the North Complex Fire on Sept. 11.
“What we’re experiencing right here is coming to a community all across the United States of America… unless we get our act together on climate change.”
I was with him all the way until he said the words “on climate change.”
As my Hoover Institution colleague Victor Davis Hanson put it last month, California is “the progressive model of the future: a once-innovative, rich state that is now a civilization in near ruins. The nation should watch us this election year and learn of its possible future.”
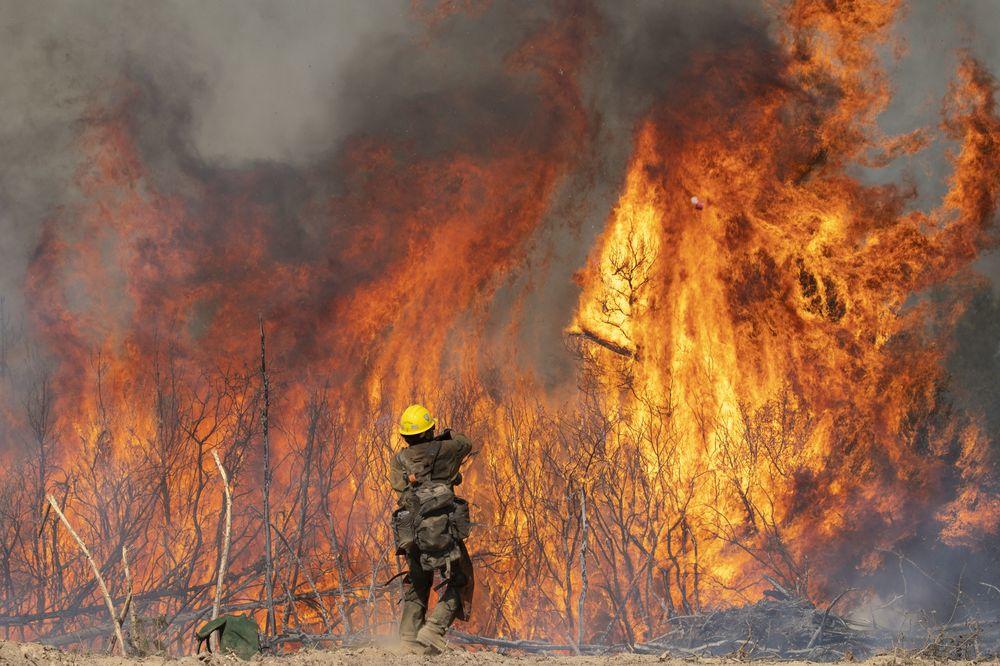
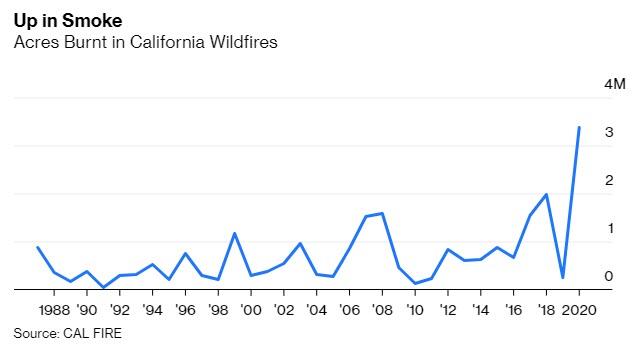
Let’s start with the fires. So far this year, they have torched more than five times as much land as the average of the previous 33 years, killing 25 people and forcing about 100,000 people from their homes. At one point, three of the largest fires in the state’s history were burning simultaneously in a ring around the San Francisco Bay Area. According to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection, or CAL FIRE, of the 10 largest fires since 1970, five broke out this year. Nine out of 10 have occurred since 2012.
No doubt high temperatures and unusual thunderstorms bear some of the responsibility for this year’s terrifying wildfires on the West Coast. It is deeply misleading to claim, as some diehard deniers still do, that temperatures aren’t rising and making wildfires more likely. But it is equally misleading to claim, as the New York Times did last week, that “scientists say” climate change “is the primary cause of the conflagration.”
In reality, as Stanford’s Rebecca Miller, Christopher Field and Katharine J. Mach argue in a recent article in Nature Sustainability, this crisis has at least as much to do with disastrous land mismanagement as with climate change, and perhaps more. Anyone who thinks solar panels, Teslas and a $3.3 billion white elephant of a high-speed rail line will avoid comparable or worse fires next year (and the year after and the year after) doesn’t understand what the scientists are really saying.
Most measures proposed by environmentalists to reduce carbon dioxide and other “greenhouse gas” emissions will pay off over 50 to 100 years, as the International Panel on Climate Change has long made clear. Even a best-case scenario of “stringent mitigation” (what the IPCC calls Representative Concentration Pathway 2.6) would not bring carbon dioxide emissions down to 1950 levels until around 2050. Nor would it lower global average temperatures; it would merely stop them rising.
And that’s only if the whole world — including China and India — takes action. California’s wildfire problem cannot be solved by the state’s citizens “getting their act together on climate change,” in Newsom’s words. The problem needs immediately effective action — and that means a return to sane forest management, if such a return is still possible. For decades, Democratic leaders in California have presided over a policy of leaving dead trees to rot, instead of the old and rational system of prescribed or controlled burns, not least because environmental and clear air regulations, as well as problems of legal liability, made controlled burns harder and harder to do.
In prehistoric California, according to a recent analysis in ProPublica, between 4.4 million and 11.8 million acres burned each year.
California’s land managers burned about 30,000 acres a year on average between 1982 and 1998. Over the next 18 years, that number dropped to an annual 13,000 acres. The result has been a huge accumulation of highly flammable kindling.
Miller, Field and Mach concluded that a total area of around 20 million acres – roughly one-fifth of the state’s territory – was in urgent need of “fuel treatment,” meaning prescribed burns, mechanical thinning and managed wildfire. It is hard to imagine anything remotely close to that happening under the current political dispensation. (The authors politely called for “fundamental shifts in prescribed-burn policies, beyond those currently under consideration.”) Or rather, it is going to happen, but at a time of Nature’s choosing, with catastrophic consequences.
A case in point: For a year and a half, red tape slowed down a forest-thinning project in Berry Creek, Butte County. The project covered just 54 acres but, thanks to the burdensome provisions of the California Environmental Quality Act, work had yet to start when the North Complex wildfire struck, devastating the town and killing 10 people.
I have some skin in this game.
Four years ago, I moved from Harvard University to Stanford University. My family traded a solid, century-old professorial residence in Cambridge for a wooden house in a wooded area that to our wooden heads seemed most idyllic. A few weeks ago, our neighborhood was on the edge of the evacuation zone.
However, I have less skin in the game than Victor Davis Hanson. He lives on the fruit and nut farm near Selma, in the Central Valley, that his family has owned since the 1870s. The air quality index in Stanford rose above 170 on three days in the last month. In Selma last week it was 460. (Anything above 301 qualifies as “emergency conditions.”)
I write these words over 1,000 miles from our California home, but it’s no good: in recent days the smoke has found us, too. Hotel parking lots full of vehicles with CA license plates confirm that we are not the only eastward migrants. It’s like Steinbeck’s “Grapes of Wrath” in reverse: Now that the Golden State is the Char-Grilled State, Californians have become the new Okies, though a good deal less impecunious.
Yet wildfires are only one of the reasons people are fleeing California.
In addition, the wrongheaded environmental policies of the sages of Sacramento have so undermined the power grid (for example, by shutting down gas-fired power plants and refusing to count hydroelectric energy as renewable) that residents have been subjected to rolling blackouts this year. The same policies have largely killed off the oil and gas industry. Newsom & Co. have failed to upgrade the water system to keep pace with the last half-century of population growth.
It’s not that California politicians don’t know how to spend money. Back in 2007, total state spending was $146 billion. Last year it was $215 billion. I know, I know: In real terms California’s GDP increased by nearly a third in the same period. And I know: If it were an independent nation it would be the fifth-largest economy in the world, ahead of India’s. But for how much longer will that be true?
California’s taxes aren’t the highest in the country — for the median household. But the tax system is one of the most progressive, with a 13.3% top tax rate on incomes above $1 million — and that’s no longer deductible from the federal tax bill as it used to be. The top 1% of taxpayers (those earning more than $500,000) now account for half of personal income-tax revenue. And there’s worse to come.
The latest brilliant ideas in Sacramento are to raise the top income rate up to 16.8% and to levy a wealth tax (0.4% on personal fortunes over $30 million) that you couldn’t even avoid paying if you left the state.
(The proposal envisages payment for up to 10 years after departure to a lower-tax state.)
It is a strange place that seeks to repel the rich while making itself a magnet for illegal immigrants by establishing no fewer than 20 “sanctuary” cities or counties.
And the results of all this progressive policy?
A poverty boom.
California now has 12% of the nation’s population, but over 30% of its welfare recipients. By the official measure, based mainly on income and family size, California’s 11.4% poverty rate in 2019 was close to the national average over the past three years. However, according to a new Census Bureau report, which takes housing and other costs into account, the real poverty rate in California is 17.2%, the highest of any state. (Newsom gets one thing right when he says, “We’re living in the wealthiest as well as the poorest state in America.”)
About a third of California’s poverty can be attributed to housing and other living costs such as clothing and utilities. As everyone who resides there knows, there’s a chronic housing shortage in the Bay Area (the median-priced home in San Francisco costs about $1.5 million), mainly because a plethora of regulations make the construction of affordable housing well-nigh impossible. In blithe disregard of all we know about rent controls — which discourage landlords from providing housing — that is, predictably, the solution the Democrats propose.
But that’s not all. The state’s public schools rank 37th in the country overall and have the highest pupil-teacher ratio.
“Only half of California students meet English standards and fewer meet math standards, test scores show,” was a headline in the Los Angeles Times last October.
Health care and pension costs are unsustainable. Oh, and they messed up on Covid-19, despite imposing the nation’s first shelter-in-place orders. Having prematurely claimed victory, California now leads New York in terms of cases, though not deaths.
Back in the 1960s, California was the world’s fantasy destination. “California Dreamin’,” “California Girls,” “Going to California” — you know the songs. But reputations have a way of outliving reality. Despite the economic miracle wrought in Silicon Valley, beginning with the genesis of the internet back in the 1970s, and despite the continuing strength of the state’s universities, the dream in terms of quality of life has slowly died.
When I first visited San Francisco in 1981, it was still one of the loveliest cities I had ever beheld. Now its streets are so filthy – human feces and syringe needles are the principal hazards – that I avoid it. (I was going to say “like the plague,” but that’s Lake Tahoe.)
Yet the Bay Area and its southern sister Los Angeles are only one of the two Californias.
As Hanson argued 10 years ago, the Central Valley is another country, more “Caribbean” or Latin American, where “countless inland communities … have become near-apartheid societies, where Spanish is the first language, the schools are not at all diverse, and the federal and state governments are either the main employers or at least the chief sources of income.”
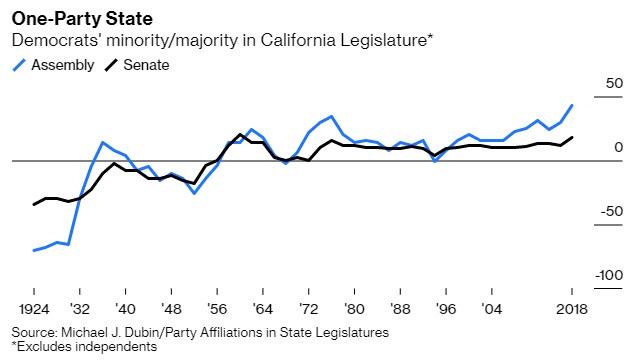
The principal reason for California’s decline is that the Golden State became a one-party state.
The Republican candidate won California in every election but one (1964) between 1952 and 1988. But the Democrat has won California in every election since, with the Democratic vote share rising from 46% in 1992 to 62% in 2016.
Democrats now have 61 out of 80 seats in the California State Assembly. The last time Republicans had a majority (of one) was in 1994, but that was an anomaly. The Democrats have essentially controlled the State Senate since 1958, with rising majorities since the 1990s. Apart from 1994, the only other year since 1958 when they did not win a majority of seats in the Assembly was 1968.
When regular voting has no effect, people eventually vote with their feet. From 2007 until 2016, about five million people moved to California but six million moved out to other states. For years before that, the newcomers were poorer than the leavers. This net exodus is surging in 2020. And businesses (for example, Charles Schwab Corp.) are leaving too. Silicon Valley is going virtual, with many big tech companies thinking of making work from home permanent for at least some employees. (One tech chief executive told me last week that his engineers were pleading not to return to the office.)
People are getting out of the Bay Area as much and perhaps more than they are getting out of New York City. Texas is only one of the favored alternatives. Realtors in Montana are reporting record demand from West Coast refugees. The hotels are full, which is unheard of at this time of year. I also know a number of eminent Californians who are now Hawaiians.
The conservative writer and broadcaster Ben Shapiro, born in L.A., just announced that he is heading to Nashville, Tennessee.
“I love the state, grew up in the state, married in the state and have had children in the state,” he told Laura Ingraham.
But California was “not a great place to raise children and not a great place to build a company.”
Now we know the true meaning of Calexit. It’s not secession. It’s exodus.
I cannot blame the leavers. When I moved West in 2016, it was in the naive belief that California was Massachusetts without snow and Stanford was Harvard with September weather all year round. How wrong I was.
But am I leaving? Well, maybe there’s no point. As Newsom’s predecessor Jerry Brown put it last week:
“There are going to be problems everywhere in the United States. This is the new normal. It’s been predicted and it’s happening … Tell me: Where are you going to go? What’s your alternative?”
Great question, but — as with Newsom’s prophecy — wrongly framed.
The big problem is not that climate change is coming to every state. It is, though most states will mitigate it better than California. The problem is that Democratic governance could be coming to the nation as a whole, starting on Jan. 20. And with the Democratic nominee, Joe Biden, turning 78 two weeks after election day, it is not a little troubling to me that his vice-presidential pick is a Californian, just as so many of his plans to spend, tax and regulate have “designed in California” all over them.
Yes, folks, California is America fast forward. Can someone please hit pause?
[MWN] – You reap what you sow!